## implementation I implemented HER solely as a replay buffer. It is done by temporarily directly re-writing transitions storage (`self._meta`) during the `sample_indices()` call. The original transitions are cached and will be restored at the beginning of the next sampling or when other methods is called. This will make sure that. for example, n-step return calculation can be done without altering the policy. There is also a problem with the original indices sampling. The sampled indices are not guaranteed to be from different episodes. So I decided to perform re-writing based on the episode. This guarantees that the sampled transitions from the same episode will have the same re-written goal. This also make the re-writing ratio calculation slightly differ from the paper, but it won't be too different if there are many episodes in the buffer. In the current commit, HER replay buffer only support 'future' strategy and online sampling. This is the best of HER in term of performance and memory efficiency. I also add a few more convenient replay buffers (`HERVectorReplayBuffer`, `HERReplayBufferManager`), test env (`MyGoalEnv`), gym wrapper (`TruncatedAsTerminated`), unit tests, and a simple example (examples/offline/fetch_her_ddpg.py). ## verification I have added unit tests for almost everything I have implemented. HER replay buffer was also tested using DDPG on [`FetchReach-v3` env](https://github.com/Farama-Foundation/Gymnasium-Robotics). I used default DDPG parameters from mujoco example and didn't tune anything further to get this good result! (train script: examples/offline/fetch_her_ddpg.py). 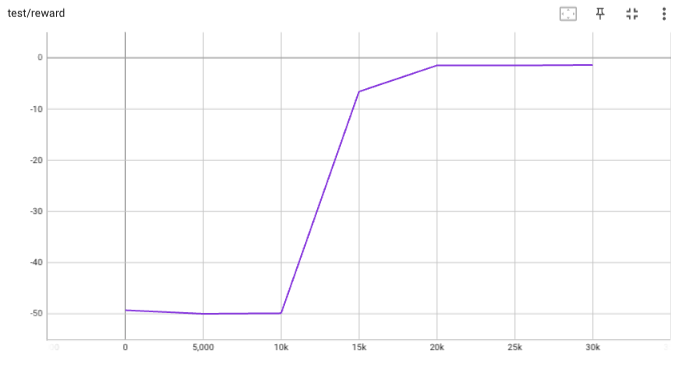
517 lines
20 KiB
Python
517 lines
20 KiB
Python
from typing import (
|
|
Any,
|
|
Callable,
|
|
Dict,
|
|
List,
|
|
Optional,
|
|
Sequence,
|
|
Tuple,
|
|
Type,
|
|
Union,
|
|
no_type_check,
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
import numpy as np
|
|
import torch
|
|
from torch import nn
|
|
|
|
from tianshou.data.batch import Batch
|
|
|
|
ModuleType = Type[nn.Module]
|
|
|
|
|
|
def miniblock(
|
|
input_size: int,
|
|
output_size: int = 0,
|
|
norm_layer: Optional[ModuleType] = None,
|
|
activation: Optional[ModuleType] = None,
|
|
linear_layer: Type[nn.Linear] = nn.Linear,
|
|
) -> List[nn.Module]:
|
|
"""Construct a miniblock with given input/output-size, norm layer and \
|
|
activation."""
|
|
layers: List[nn.Module] = [linear_layer(input_size, output_size)]
|
|
if norm_layer is not None:
|
|
layers += [norm_layer(output_size)] # type: ignore
|
|
if activation is not None:
|
|
layers += [activation()]
|
|
return layers
|
|
|
|
|
|
class MLP(nn.Module):
|
|
"""Simple MLP backbone.
|
|
|
|
Create a MLP of size input_dim * hidden_sizes[0] * hidden_sizes[1] * ...
|
|
* hidden_sizes[-1] * output_dim
|
|
|
|
:param int input_dim: dimension of the input vector.
|
|
:param int output_dim: dimension of the output vector. If set to 0, there
|
|
is no final linear layer.
|
|
:param hidden_sizes: shape of MLP passed in as a list, not including
|
|
input_dim and output_dim.
|
|
:param norm_layer: use which normalization before activation, e.g.,
|
|
``nn.LayerNorm`` and ``nn.BatchNorm1d``. Default to no normalization.
|
|
You can also pass a list of normalization modules with the same length
|
|
of hidden_sizes, to use different normalization module in different
|
|
layers. Default to no normalization.
|
|
:param activation: which activation to use after each layer, can be both
|
|
the same activation for all layers if passed in nn.Module, or different
|
|
activation for different Modules if passed in a list. Default to
|
|
nn.ReLU.
|
|
:param device: which device to create this model on. Default to None.
|
|
:param linear_layer: use this module as linear layer. Default to nn.Linear.
|
|
:param bool flatten_input: whether to flatten input data. Default to True.
|
|
"""
|
|
|
|
def __init__(
|
|
self,
|
|
input_dim: int,
|
|
output_dim: int = 0,
|
|
hidden_sizes: Sequence[int] = (),
|
|
norm_layer: Optional[Union[ModuleType, Sequence[ModuleType]]] = None,
|
|
activation: Optional[Union[ModuleType, Sequence[ModuleType]]] = nn.ReLU,
|
|
device: Optional[Union[str, int, torch.device]] = None,
|
|
linear_layer: Type[nn.Linear] = nn.Linear,
|
|
flatten_input: bool = True,
|
|
) -> None:
|
|
super().__init__()
|
|
self.device = device
|
|
if norm_layer:
|
|
if isinstance(norm_layer, list):
|
|
assert len(norm_layer) == len(hidden_sizes)
|
|
norm_layer_list = norm_layer
|
|
else:
|
|
norm_layer_list = [norm_layer for _ in range(len(hidden_sizes))]
|
|
else:
|
|
norm_layer_list = [None] * len(hidden_sizes)
|
|
if activation:
|
|
if isinstance(activation, list):
|
|
assert len(activation) == len(hidden_sizes)
|
|
activation_list = activation
|
|
else:
|
|
activation_list = [activation for _ in range(len(hidden_sizes))]
|
|
else:
|
|
activation_list = [None] * len(hidden_sizes)
|
|
hidden_sizes = [input_dim] + list(hidden_sizes)
|
|
model = []
|
|
for in_dim, out_dim, norm, activ in zip(
|
|
hidden_sizes[:-1], hidden_sizes[1:], norm_layer_list, activation_list
|
|
):
|
|
model += miniblock(in_dim, out_dim, norm, activ, linear_layer)
|
|
if output_dim > 0:
|
|
model += [linear_layer(hidden_sizes[-1], output_dim)]
|
|
self.output_dim = output_dim or hidden_sizes[-1]
|
|
self.model = nn.Sequential(*model)
|
|
self.flatten_input = flatten_input
|
|
|
|
@no_type_check
|
|
def forward(self, obs: Union[np.ndarray, torch.Tensor]) -> torch.Tensor:
|
|
if self.device is not None:
|
|
obs = torch.as_tensor(obs, device=self.device, dtype=torch.float32)
|
|
if self.flatten_input:
|
|
obs = obs.flatten(1)
|
|
return self.model(obs)
|
|
|
|
|
|
class Net(nn.Module):
|
|
"""Wrapper of MLP to support more specific DRL usage.
|
|
|
|
For advanced usage (how to customize the network), please refer to
|
|
:ref:`build_the_network`.
|
|
|
|
:param state_shape: int or a sequence of int of the shape of state.
|
|
:param action_shape: int or a sequence of int of the shape of action.
|
|
:param hidden_sizes: shape of MLP passed in as a list.
|
|
:param norm_layer: use which normalization before activation, e.g.,
|
|
``nn.LayerNorm`` and ``nn.BatchNorm1d``. Default to no normalization.
|
|
You can also pass a list of normalization modules with the same length
|
|
of hidden_sizes, to use different normalization module in different
|
|
layers. Default to no normalization.
|
|
:param activation: which activation to use after each layer, can be both
|
|
the same activation for all layers if passed in nn.Module, or different
|
|
activation for different Modules if passed in a list. Default to
|
|
nn.ReLU.
|
|
:param device: specify the device when the network actually runs. Default
|
|
to "cpu".
|
|
:param bool softmax: whether to apply a softmax layer over the last layer's
|
|
output.
|
|
:param bool concat: whether the input shape is concatenated by state_shape
|
|
and action_shape. If it is True, ``action_shape`` is not the output
|
|
shape, but affects the input shape only.
|
|
:param int num_atoms: in order to expand to the net of distributional RL.
|
|
Default to 1 (not use).
|
|
:param bool dueling_param: whether to use dueling network to calculate Q
|
|
values (for Dueling DQN). If you want to use dueling option, you should
|
|
pass a tuple of two dict (first for Q and second for V) stating
|
|
self-defined arguments as stated in
|
|
class:`~tianshou.utils.net.common.MLP`. Default to None.
|
|
:param linear_layer: use this module as linear layer. Default to nn.Linear.
|
|
|
|
.. seealso::
|
|
|
|
Please refer to :class:`~tianshou.utils.net.common.MLP` for more
|
|
detailed explanation on the usage of activation, norm_layer, etc.
|
|
|
|
You can also refer to :class:`~tianshou.utils.net.continuous.Actor`,
|
|
:class:`~tianshou.utils.net.continuous.Critic`, etc, to see how it's
|
|
suggested be used.
|
|
"""
|
|
|
|
def __init__(
|
|
self,
|
|
state_shape: Union[int, Sequence[int]],
|
|
action_shape: Union[int, Sequence[int]] = 0,
|
|
hidden_sizes: Sequence[int] = (),
|
|
norm_layer: Optional[ModuleType] = None,
|
|
activation: Optional[ModuleType] = nn.ReLU,
|
|
device: Union[str, int, torch.device] = "cpu",
|
|
softmax: bool = False,
|
|
concat: bool = False,
|
|
num_atoms: int = 1,
|
|
dueling_param: Optional[Tuple[Dict[str, Any], Dict[str, Any]]] = None,
|
|
linear_layer: Type[nn.Linear] = nn.Linear,
|
|
) -> None:
|
|
super().__init__()
|
|
self.device = device
|
|
self.softmax = softmax
|
|
self.num_atoms = num_atoms
|
|
input_dim = int(np.prod(state_shape))
|
|
action_dim = int(np.prod(action_shape)) * num_atoms
|
|
if concat:
|
|
input_dim += action_dim
|
|
self.use_dueling = dueling_param is not None
|
|
output_dim = action_dim if not self.use_dueling and not concat else 0
|
|
self.model = MLP(
|
|
input_dim, output_dim, hidden_sizes, norm_layer, activation, device,
|
|
linear_layer
|
|
)
|
|
self.output_dim = self.model.output_dim
|
|
if self.use_dueling: # dueling DQN
|
|
q_kwargs, v_kwargs = dueling_param # type: ignore
|
|
q_output_dim, v_output_dim = 0, 0
|
|
if not concat:
|
|
q_output_dim, v_output_dim = action_dim, num_atoms
|
|
q_kwargs: Dict[str, Any] = {
|
|
**q_kwargs, "input_dim": self.output_dim,
|
|
"output_dim": q_output_dim,
|
|
"device": self.device
|
|
}
|
|
v_kwargs: Dict[str, Any] = {
|
|
**v_kwargs, "input_dim": self.output_dim,
|
|
"output_dim": v_output_dim,
|
|
"device": self.device
|
|
}
|
|
self.Q, self.V = MLP(**q_kwargs), MLP(**v_kwargs)
|
|
self.output_dim = self.Q.output_dim
|
|
|
|
def forward(
|
|
self,
|
|
obs: Union[np.ndarray, torch.Tensor],
|
|
state: Any = None,
|
|
info: Dict[str, Any] = {},
|
|
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Any]:
|
|
"""Mapping: obs -> flatten (inside MLP)-> logits."""
|
|
logits = self.model(obs)
|
|
bsz = logits.shape[0]
|
|
if self.use_dueling: # Dueling DQN
|
|
q, v = self.Q(logits), self.V(logits)
|
|
if self.num_atoms > 1:
|
|
q = q.view(bsz, -1, self.num_atoms)
|
|
v = v.view(bsz, -1, self.num_atoms)
|
|
logits = q - q.mean(dim=1, keepdim=True) + v
|
|
elif self.num_atoms > 1:
|
|
logits = logits.view(bsz, -1, self.num_atoms)
|
|
if self.softmax:
|
|
logits = torch.softmax(logits, dim=-1)
|
|
return logits, state
|
|
|
|
|
|
class Recurrent(nn.Module):
|
|
"""Simple Recurrent network based on LSTM.
|
|
|
|
For advanced usage (how to customize the network), please refer to
|
|
:ref:`build_the_network`.
|
|
"""
|
|
|
|
def __init__(
|
|
self,
|
|
layer_num: int,
|
|
state_shape: Union[int, Sequence[int]],
|
|
action_shape: Union[int, Sequence[int]],
|
|
device: Union[str, int, torch.device] = "cpu",
|
|
hidden_layer_size: int = 128,
|
|
) -> None:
|
|
super().__init__()
|
|
self.device = device
|
|
self.nn = nn.LSTM(
|
|
input_size=hidden_layer_size,
|
|
hidden_size=hidden_layer_size,
|
|
num_layers=layer_num,
|
|
batch_first=True,
|
|
)
|
|
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(int(np.prod(state_shape)), hidden_layer_size)
|
|
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_layer_size, int(np.prod(action_shape)))
|
|
|
|
def forward(
|
|
self,
|
|
obs: Union[np.ndarray, torch.Tensor],
|
|
state: Optional[Dict[str, torch.Tensor]] = None,
|
|
info: Dict[str, Any] = {},
|
|
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Dict[str, torch.Tensor]]:
|
|
"""Mapping: obs -> flatten -> logits.
|
|
|
|
In the evaluation mode, `obs` should be with shape ``[bsz, dim]``; in the
|
|
training mode, `obs` should be with shape ``[bsz, len, dim]``. See the code
|
|
and comment for more detail.
|
|
"""
|
|
obs = torch.as_tensor(
|
|
obs,
|
|
device=self.device,
|
|
dtype=torch.float32,
|
|
)
|
|
# obs [bsz, len, dim] (training) or [bsz, dim] (evaluation)
|
|
# In short, the tensor's shape in training phase is longer than which
|
|
# in evaluation phase.
|
|
if len(obs.shape) == 2:
|
|
obs = obs.unsqueeze(-2)
|
|
obs = self.fc1(obs)
|
|
self.nn.flatten_parameters()
|
|
if state is None:
|
|
obs, (hidden, cell) = self.nn(obs)
|
|
else:
|
|
# we store the stack data in [bsz, len, ...] format
|
|
# but pytorch rnn needs [len, bsz, ...]
|
|
obs, (hidden, cell) = self.nn(
|
|
obs, (
|
|
state["hidden"].transpose(0, 1).contiguous(),
|
|
state["cell"].transpose(0, 1).contiguous()
|
|
)
|
|
)
|
|
obs = self.fc2(obs[:, -1])
|
|
# please ensure the first dim is batch size: [bsz, len, ...]
|
|
return obs, {
|
|
"hidden": hidden.transpose(0, 1).detach(),
|
|
"cell": cell.transpose(0, 1).detach()
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
class ActorCritic(nn.Module):
|
|
"""An actor-critic network for parsing parameters.
|
|
|
|
Using ``actor_critic.parameters()`` instead of set.union or list+list to avoid
|
|
issue #449.
|
|
|
|
:param nn.Module actor: the actor network.
|
|
:param nn.Module critic: the critic network.
|
|
"""
|
|
|
|
def __init__(self, actor: nn.Module, critic: nn.Module) -> None:
|
|
super().__init__()
|
|
self.actor = actor
|
|
self.critic = critic
|
|
|
|
|
|
class DataParallelNet(nn.Module):
|
|
"""DataParallel wrapper for training agent with multi-GPU.
|
|
|
|
This class does only the conversion of input data type, from numpy array to torch's
|
|
Tensor. If the input is a nested dictionary, the user should create a similar class
|
|
to do the same thing.
|
|
|
|
:param nn.Module net: the network to be distributed in different GPUs.
|
|
"""
|
|
|
|
def __init__(self, net: nn.Module) -> None:
|
|
super().__init__()
|
|
self.net = nn.DataParallel(net)
|
|
|
|
def forward(self, obs: Union[np.ndarray, torch.Tensor], *args: Any,
|
|
**kwargs: Any) -> Tuple[Any, Any]:
|
|
if not isinstance(obs, torch.Tensor):
|
|
obs = torch.as_tensor(obs, dtype=torch.float32)
|
|
return self.net(obs=obs.cuda(), *args, **kwargs)
|
|
|
|
|
|
class EnsembleLinear(nn.Module):
|
|
"""Linear Layer of Ensemble network.
|
|
|
|
:param int ensemble_size: Number of subnets in the ensemble.
|
|
:param int inp_feature: dimension of the input vector.
|
|
:param int out_feature: dimension of the output vector.
|
|
:param bool bias: whether to include an additive bias, default to be True.
|
|
"""
|
|
|
|
def __init__(
|
|
self,
|
|
ensemble_size: int,
|
|
in_feature: int,
|
|
out_feature: int,
|
|
bias: bool = True,
|
|
) -> None:
|
|
super().__init__()
|
|
|
|
# To be consistent with PyTorch default initializer
|
|
k = np.sqrt(1. / in_feature)
|
|
weight_data = torch.rand((ensemble_size, in_feature, out_feature)) * 2 * k - k
|
|
self.weight = nn.Parameter(weight_data, requires_grad=True)
|
|
|
|
self.bias: Union[nn.Parameter, None]
|
|
if bias:
|
|
bias_data = torch.rand((ensemble_size, 1, out_feature)) * 2 * k - k
|
|
self.bias = nn.Parameter(bias_data, requires_grad=True)
|
|
else:
|
|
self.bias = None
|
|
|
|
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
|
|
x = torch.matmul(x, self.weight)
|
|
if self.bias is not None:
|
|
x = x + self.bias
|
|
return x
|
|
|
|
|
|
class BranchingNet(nn.Module):
|
|
"""Branching dual Q network.
|
|
|
|
Network for the BranchingDQNPolicy, it uses a common network module, a value module
|
|
and action "branches" one for each dimension.It allows for a linear scaling
|
|
of Q-value the output w.r.t. the number of dimensions in the action space.
|
|
For more info please refer to: arXiv:1711.08946.
|
|
:param state_shape: int or a sequence of int of the shape of state.
|
|
:param action_shape: int or a sequence of int of the shape of action.
|
|
:param action_peer_branch: int or a sequence of int of the number of actions in
|
|
each dimension.
|
|
:param common_hidden_sizes: shape of the common MLP network passed in as a list.
|
|
:param value_hidden_sizes: shape of the value MLP network passed in as a list.
|
|
:param action_hidden_sizes: shape of the action MLP network passed in as a list.
|
|
:param norm_layer: use which normalization before activation, e.g.,
|
|
``nn.LayerNorm`` and ``nn.BatchNorm1d``. Default to no normalization.
|
|
You can also pass a list of normalization modules with the same length
|
|
of hidden_sizes, to use different normalization module in different
|
|
layers. Default to no normalization.
|
|
:param activation: which activation to use after each layer, can be both
|
|
the same activation for all layers if passed in nn.Module, or different
|
|
activation for different Modules if passed in a list. Default to
|
|
nn.ReLU.
|
|
:param device: specify the device when the network actually runs. Default
|
|
to "cpu".
|
|
:param bool softmax: whether to apply a softmax layer over the last layer's
|
|
output.
|
|
"""
|
|
|
|
def __init__(
|
|
self,
|
|
state_shape: Union[int, Sequence[int]],
|
|
num_branches: int = 0,
|
|
action_per_branch: int = 2,
|
|
common_hidden_sizes: List[int] = [],
|
|
value_hidden_sizes: List[int] = [],
|
|
action_hidden_sizes: List[int] = [],
|
|
norm_layer: Optional[ModuleType] = None,
|
|
activation: Optional[ModuleType] = nn.ReLU,
|
|
device: Union[str, int, torch.device] = "cpu",
|
|
) -> None:
|
|
super().__init__()
|
|
self.device = device
|
|
self.num_branches = num_branches
|
|
self.action_per_branch = action_per_branch
|
|
# common network
|
|
common_input_dim = int(np.prod(state_shape))
|
|
common_output_dim = 0
|
|
self.common = MLP(
|
|
common_input_dim, common_output_dim, common_hidden_sizes, norm_layer,
|
|
activation, device
|
|
)
|
|
# value network
|
|
value_input_dim = common_hidden_sizes[-1]
|
|
value_output_dim = 1
|
|
self.value = MLP(
|
|
value_input_dim, value_output_dim, value_hidden_sizes, norm_layer,
|
|
activation, device
|
|
)
|
|
# action branching network
|
|
action_input_dim = common_hidden_sizes[-1]
|
|
action_output_dim = action_per_branch
|
|
self.branches = nn.ModuleList(
|
|
[
|
|
MLP(
|
|
action_input_dim, action_output_dim, action_hidden_sizes,
|
|
norm_layer, activation, device
|
|
) for _ in range(self.num_branches)
|
|
]
|
|
)
|
|
|
|
def forward(
|
|
self,
|
|
obs: Union[np.ndarray, torch.Tensor],
|
|
state: Any = None,
|
|
info: Dict[str, Any] = {},
|
|
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Any]:
|
|
"""Mapping: obs -> model -> logits."""
|
|
common_out = self.common(obs)
|
|
value_out = self.value(common_out)
|
|
value_out = torch.unsqueeze(value_out, 1)
|
|
action_out = []
|
|
for b in self.branches:
|
|
action_out.append(b(common_out))
|
|
action_scores = torch.stack(action_out, 1)
|
|
action_scores = action_scores - torch.mean(action_scores, 2, keepdim=True)
|
|
logits = value_out + action_scores
|
|
return logits, state
|
|
|
|
|
|
def get_dict_state_decorator(
|
|
state_shape: Dict[str, Union[int, Sequence[int]]], keys: Sequence[str]
|
|
) -> Tuple[Callable, int]:
|
|
"""A helper function to make Net or equivalent classes (e.g. Actor, Critic) \
|
|
applicable to dict state.
|
|
|
|
The first return item, ``decorator_fn``, will alter the implementation of forward
|
|
function of the given class by preprocessing the observation. The preprocessing is
|
|
basically flatten the observation and concatenate them based on the ``keys`` order.
|
|
The batch dimension is preserved if presented. The result observation shape will
|
|
be equal to ``new_state_shape``, the second return item.
|
|
|
|
:param state_shape: A dictionary indicating each state's shape
|
|
:param keys: A list of state's keys. The flatten observation will be according to \
|
|
this list order.
|
|
:returns: a 2-items tuple ``decorator_fn`` and ``new_state_shape``
|
|
"""
|
|
original_shape = state_shape
|
|
flat_state_shapes = []
|
|
for k in keys:
|
|
flat_state_shapes.append(int(np.prod(state_shape[k])))
|
|
new_state_shape = sum(flat_state_shapes)
|
|
|
|
def preprocess_obs(
|
|
obs: Union[Batch, dict, torch.Tensor, np.ndarray]
|
|
) -> torch.Tensor:
|
|
if isinstance(obs, dict) or (isinstance(obs, Batch) and keys[0] in obs):
|
|
if original_shape[keys[0]] == obs[keys[0]].shape:
|
|
# No batch dim
|
|
new_obs = torch.Tensor([obs[k] for k in keys]).flatten()
|
|
# new_obs = torch.Tensor([obs[k] for k in keys]).reshape(1, -1)
|
|
else:
|
|
bsz = obs[keys[0]].shape[0]
|
|
new_obs = torch.cat(
|
|
[torch.Tensor(obs[k].reshape(bsz, -1)) for k in keys], dim=1
|
|
)
|
|
else:
|
|
new_obs = torch.Tensor(obs)
|
|
return new_obs
|
|
|
|
@no_type_check
|
|
def decorator_fn(net_class):
|
|
|
|
class new_net_class(net_class):
|
|
|
|
def forward(
|
|
self,
|
|
obs: Union[np.ndarray, torch.Tensor],
|
|
*args,
|
|
**kwargs,
|
|
) -> Any:
|
|
return super().forward(preprocess_obs(obs), *args, **kwargs)
|
|
|
|
return new_net_class
|
|
|
|
return decorator_fn, new_state_shape
|